What is Quality?
What is Quality Various Definitions of Quality The word “Quality” has different meanings for different…
There is always confusion about which activity is called Rework and which is known as repair. After going through this post, it will be very clear in your mind about the concept of Rework and Repair.
Let us understand the outcome of any Inspection. When we perform Inspection on any Product, mainly there will be following outcome.
Either Product will be:
> Conforming
> Nonconforming
 |
| Outcome of Inspection |
In case of conforming product (OK product), it will be dispatched to customer. But Nonconforming product cannot be dispatched. We have to Hold it till further decision.
Now, Nonconforming Product may be mainly of three types:
> Can be Reworked
> Can be Repaired
> Cannot Rework or Repair (Reject)
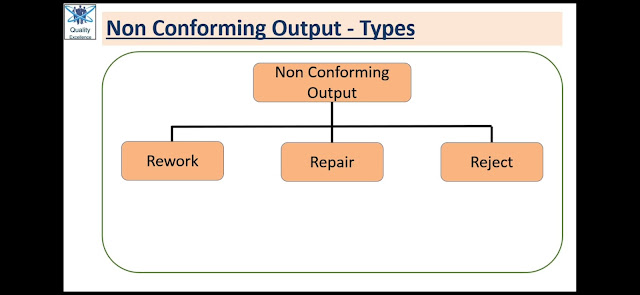 |
| Types of Nonconforming Outputs |
We have not considered here 2nd sale or degrading of Product.
Now, let us understand the definition of Rework and Repair as per ISO 9000 standard
Action on a non-conforming product or service to make it to confirm to the requirements.
Any activity or action taken on the Product or service to make it to conform as per customers requirement (i.e. as per Drawing, standards, specifications, etc..). That activity or action is termed as Rework Activity or Rework Action.
Note: After Rework, Product will be 100% conforming to the requirements of the customer.
Action on a non-conforming product or service to make it acceptable for the intended use.
A successful repair of a non-conforming product or service does not necessarily make the product or service conform to the requirements.
It can be that in conjunction with a repair a concession is required.
Any activity or action taken on the Product or service to make it functionally usable. That activity or action is termed as Repair Activity or Repair Action.
Before performing repair activity, customer approval (Concession / Deviation) is required. After Approval of Concession / Deviation, repair activity can be started.
In IATF 16949 : 2016 version, there is a reference of Rework as mentioned below
The organisation shall utilise risk analysis (such as FMEA) methodology to assess risks in the rework process prior to a decision to rework the product.
Before taking decision of performing Rework activity on Product, organisation must assess risks (by risk analysis methodology like FMEA) involved in Rework Process.
The organisation shall utilise risk analysis (such as FMEA) methodology to assess risks in the repair process prior to a decision to repair the product.
Before taking decision of performing Repair activity on Product, organisation must assess risks (by risk analysis methodology like FMEA) involved in Repair Process.
Now let us understand the same through some Examples
Required Outer diameter of a Product as per customer Requirement (mentioned in Customer Drawing) is 50 ± 0.2mm
During Inspection, one Product observed with Outer Diameter = 51.20mm (Diameter is oversize and is not as per customer requirement). This product is termed as Non-conforming Product and cannot be dispatched to Customer.
As this Diameter is Oversize and have extra material to remove on OD, it can be re-machined to make it conform to Drawing requirements and in turn customer requirement.
After Re-machining, Diameter observed is 50.10mm which is as per Customer requirement.
After re-machining, the Product now is a conforming Product.
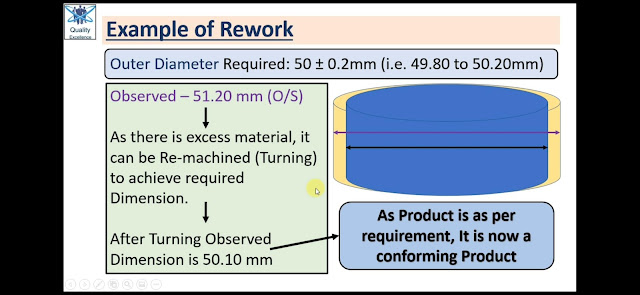 |
| Example of Rework |
Above activity or action performed on nonconforming Product (Re-machining) is termed as Rework.
Let us take the same Product Data for Repair example also
Required Outer diameter of a Product as per customer Requirement (mentioned in Customer Drawing) is 50 ± 0.2mm
During Inspection, one Product observed with Outer Diameter = 49.60mm (Diameter is undersize and is not as per customer requirement). This product is termed as Non-conforming Product and cannot be dispatched to Customer.
As this Diameter is Undersize and have No extra material to remove on OD, it cannot be re-machined.
We must approach to customer for Concession / Deviation (welding on OD and then again re-machining to achieve required OD). If customer approves the same then perform the activity on the Product.
After welding and re-machining, the Product now is functionally usable but not as per the customer requirement as we have carried out Welding.
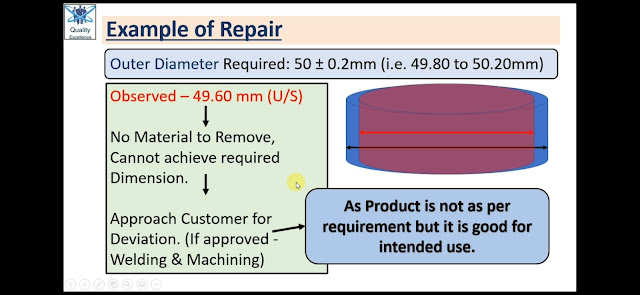 |
Example of Repair |
Above activity or action performed on nonconforming Product (Welding & Re-machining) is termed as Repair.
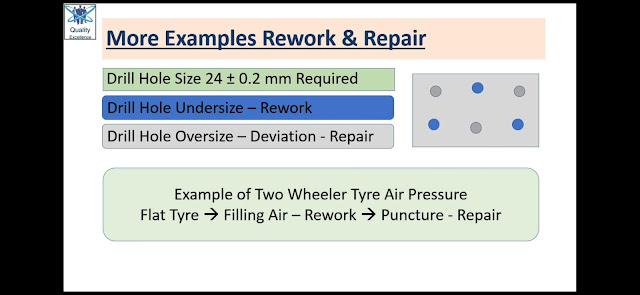
On a Rectangular MS Plate 3 Holes of Diameter 24 ± 0.2mm to be drilled. In one Product, it was observed that Drill Holes were Undersize (23.6mm).
With Re-drilling of required Size, part can be a conforming Product. This activity is termed as Rework.
On a Rectangular MS Plate 3 Holes of Diameter 24 ± 0.2mm to be drilled. In one Product, it was observed that Drill Holes were Oversize (24.6mm).
In above case we must approach to customer whether we can Plug these holes and Drill new Holes as per required Size.
If customer approves this Deviation, we can Plug deviated Holes and Drill fresh Holes. In this case Product will be functionally usable but it is not as per the customer requirement.Above activity is termed as Repair.
 |
Example of Rework and Repair |
If your two-wheeler tyre is flat and there is no air in the tyre. You approach to Puncture shop.
Shop owner checks the tube and does not find any air leakage. He refills the air and hand over to you. This activity is termed as rework.
Suppose he finds air leakage and if there is a puncture he will show you puncture in the tube and with your permission (Deviation) he will seal the puncture, refill the air and handover to you. This activity is termed as Repair.
Hope you have understood Rework and Repair with above Examples.
Now let us summarise Overall activity / Flow of Inspection outputs
 |
Nonconforming Output types and actions |
Now let us summaries the Difference between Rework and Repair or Rework vs Repair
> 100% conform to requirements
> Customer approval not required. (Exception)
> Documented Approval not required from Customer
> Low Risk – It meets requirements.
> It is good for intended use. (Functional)
> Customer approval required. (Must)
> Doc. Approval reqd. from Customer.
> High Risk – Chances of Field Failures
Feel free to comment below if you wish to know difference between any other term, I will prepare a separate post on that Topic.
Thanks and Happy Learning Ahead…….